On Exhibit
Delta Country
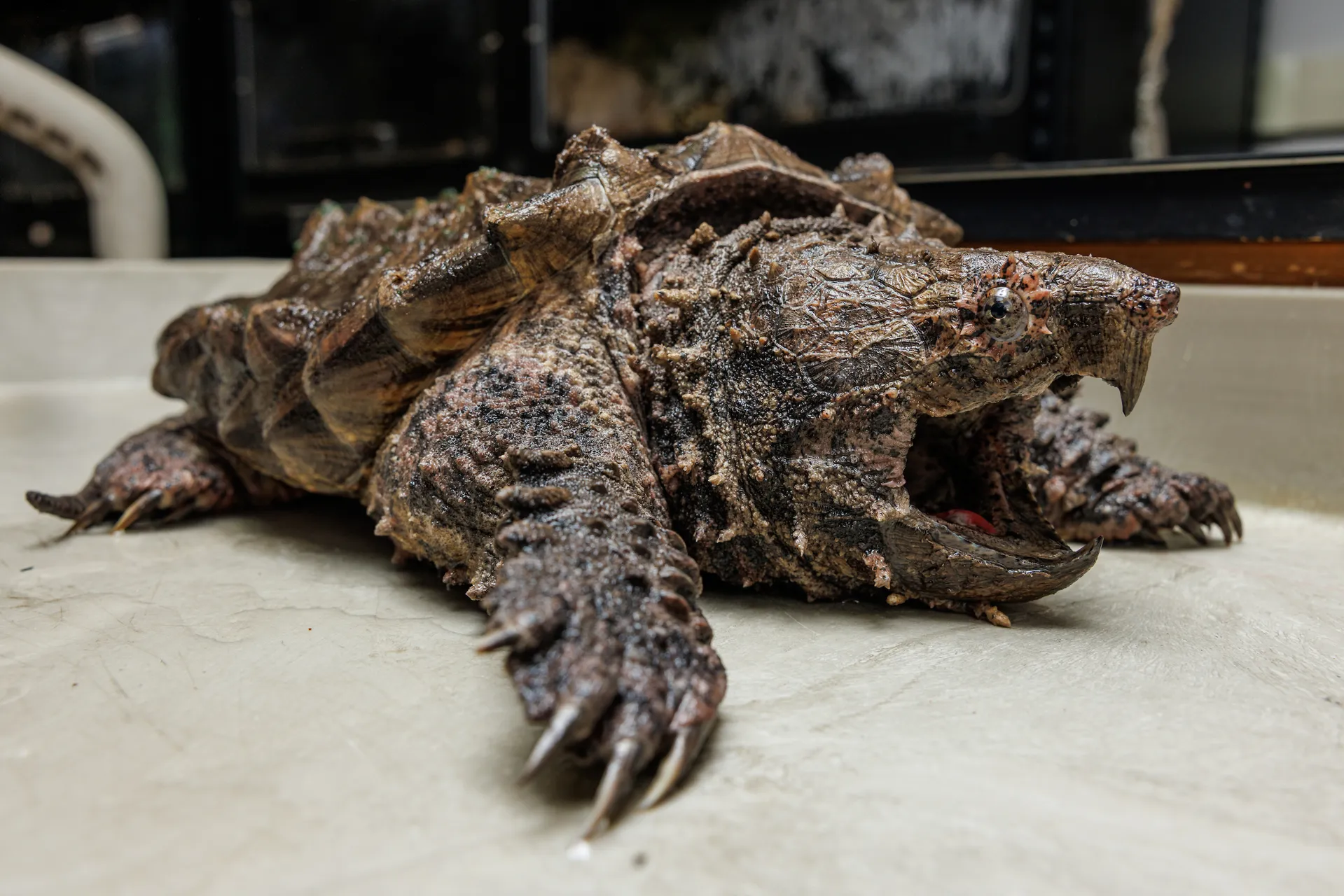
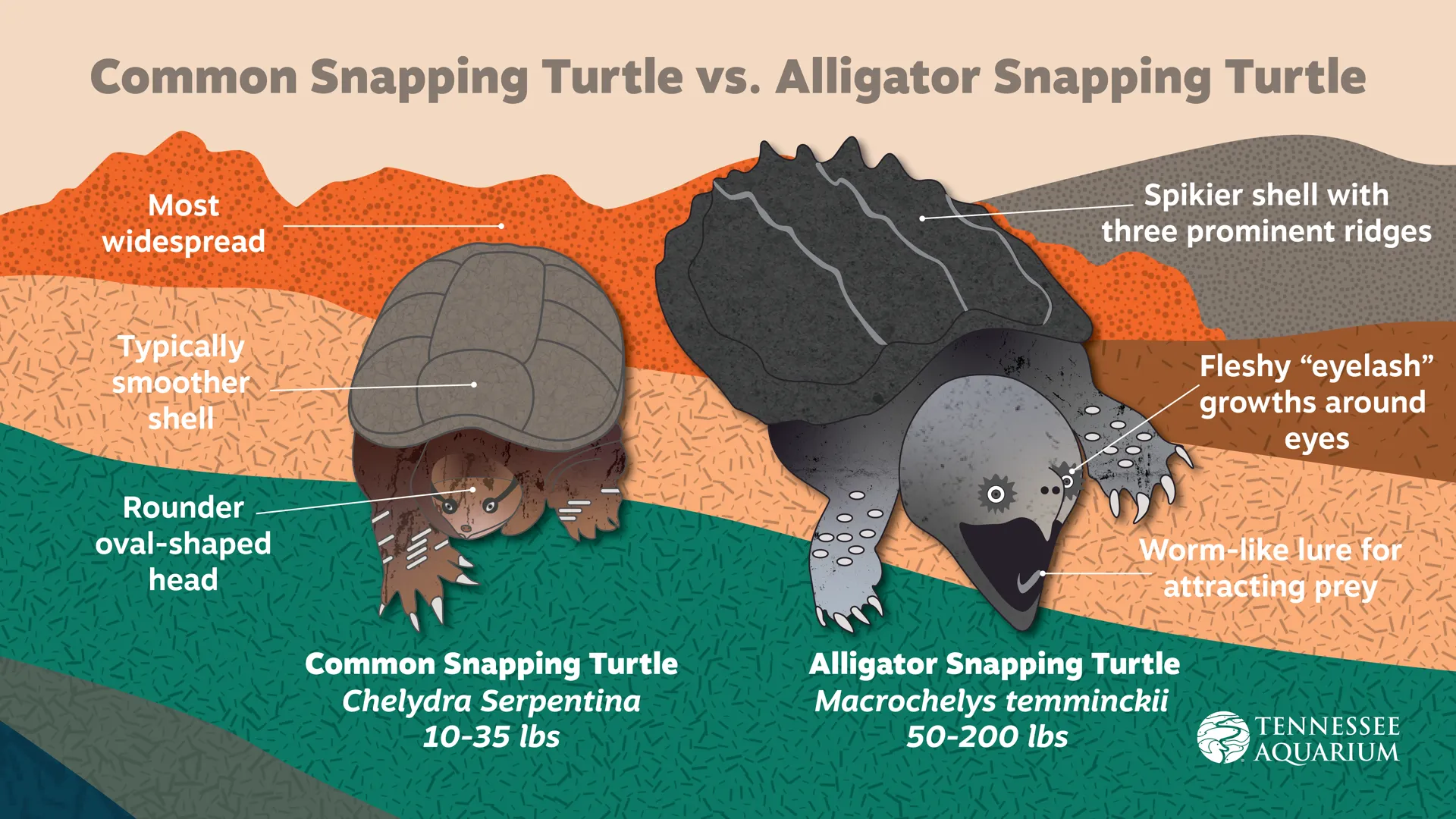
Alligator snapping turtles live in rivers whose water drains into the Gulf of Mexico. The adults hunt in the deep water of rivers, lakes, swamps, ponds and bayous where plants and algae enhance their camouflage. Best known for an adaptation that allows it to lure fish into its mouth, the alligator snapper is a bottom dweller that surfaces to breathe. To catch a fish, the turtle will sit very still in the depths of a pond or river for up to 50 minutes. There it waits patiently, holding its mouth open and wiggling the small, pink, worm-like appendage on its tongue to lure passing fish. And if a fish sees the fake worm and swims in to eat it...Wham! The fish becomes the dinner instead of the diner!